By Emmanuel Monneret (CERN)
As of early June, the HL-LHC Cryogenics project reached a new important milestone with the launch of installation activities for the helium refrigeration plants. Two helium cryogenic plants—each delivering 14 kW equivalent at 4.5 K, including 3.25 kW at 1.9 K—will be installed at HL-LHC Point 1 and Point 5. These systems will deliver the cryogenic cooling capacity required for the new superconducting magnets, radiofrequency crab cavities, and cold powering systems.
Each plant comprises several key systems: a helium compressor station located in the SHM building, a 4.5 K cold box (housing key elements such heat exchangers and turbo-expanders) in the SD building, and a cold compressor box—delivering cooling at 1.9 K—installed in the US cavern. The 4.5 K cold box and the cold compressor box are connected via a vertical cryogenic transfer line located within the PM shaft.
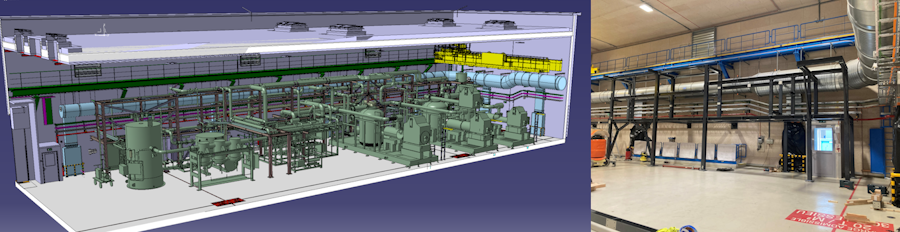
3D model of the compressor station versus installation of steel structure in SHM17 building
Installation officially kicked off in June with the arrival at CERN of our industrial partner, Linde Kryotechnik AG, who supervises the assembly of the steel framework that will support the piping infrastructure. The next major milestone is scheduled towards the end of the summer, with the planned installation of the helium compressor skids and the 4.5 K cold box.

